WHAT IS PUBLIC CLOUD?

The most recognisable model of cloud computing to many consumers is the public cloud model, under which cloud services are provided in a virtualised environment, constructed using pooled shared physical resources, and accessible over a public network such as the internet.
A public cloud is one based on the standard cloud computing model, in which a service provider makes resources, such as virtual machines (VMs), applications or storage, available to the general public over the internet. Public cloud services may be free or offered on a pay-per-usage model.
The main benefits of using a public cloud service are:
- it reduces the need for organizations to invest in and maintain their own on-premises IT resources;
- it enables scalability to meet workload and user demands; and
- there are fewer wasted resources because customers only pay for the resources they use.
Public cloud architecture
Public cloud is a fully virtualized environment. In addition, providers have a multi-tenant architecture that enables users -- or tenants -- to share computing resources. Each tenant's data in the public cloud, however, remains isolated from other tenants. Public cloud also relies on high-bandwidth network connectivity to rapidly transmit data.
Public cloud storage is typically redundant, using multiple data centers and careful replication of file versions. This characteristic has given it a reputation for resiliency.
Public cloud architecture can be further categorized by service model. Common service models include:
- software as a service (SaaS), in which a third-party provider hosts applications and makes them available to customers over the internet;
- platform as a service (PaaS), in which a third-party provider delivers hardware and software tools -- usually those needed for application development -- to its users as a service; and
- infrastructure as a service (IaaS), in which a third-party provider offers virtualized computing resources, such as VMs and storage, over the internet.
Public cloud pros and cons
In general, the public cloud is seen as a way for enterprises to scale IT resources on demand, without having to maintain as many infrastructure components, applications or development resources in house.
The pay-per-usage pricing structure offered by most public cloud providers is also seen by some enterprises as an attractive and more flexible financial model. For example, organizations account for their public cloud service as an operational or variable cost rather than as a capital or fixed cost. In some cases, this means organizations do not require lengthy reviews or advanced budget planning for public cloud decisions.
However, because users typically deploy public cloud services in a self-service model, some companies find it difficult to accurately track cloud service usage, and potentially end up paying for more cloud resources than they actually need. Some organizations also just prefer to directly supervise and manage their own on-premises IT resources, including servers.
In addition, because of the multi-tenant nature of public cloud, security is an ongoing concern for some enterprises evaluating the cloud. While public cloud providers offer security technologies, such as encryption and identity and access management tools, some organizations -- especially those with strict regulatory or governance requirements -- choose to keep workloads on premises.
The pay-per-usage pricing structure offered by most public cloud providers is also seen by some enterprises as an attractive and more flexible financial model. For example, organizations account for their public cloud service as an operational or variable cost rather than as a capital or fixed cost. In some cases, this means organizations do not require lengthy reviews or advanced budget planning for public cloud decisions.
However, because users typically deploy public cloud services in a self-service model, some companies find it difficult to accurately track cloud service usage, and potentially end up paying for more cloud resources than they actually need. Some organizations also just prefer to directly supervise and manage their own on-premises IT resources, including servers.
In addition, because of the multi-tenant nature of public cloud, security is an ongoing concern for some enterprises evaluating the cloud. While public cloud providers offer security technologies, such as encryption and identity and access management tools, some organizations -- especially those with strict regulatory or governance requirements -- choose to keep workloads on premises.
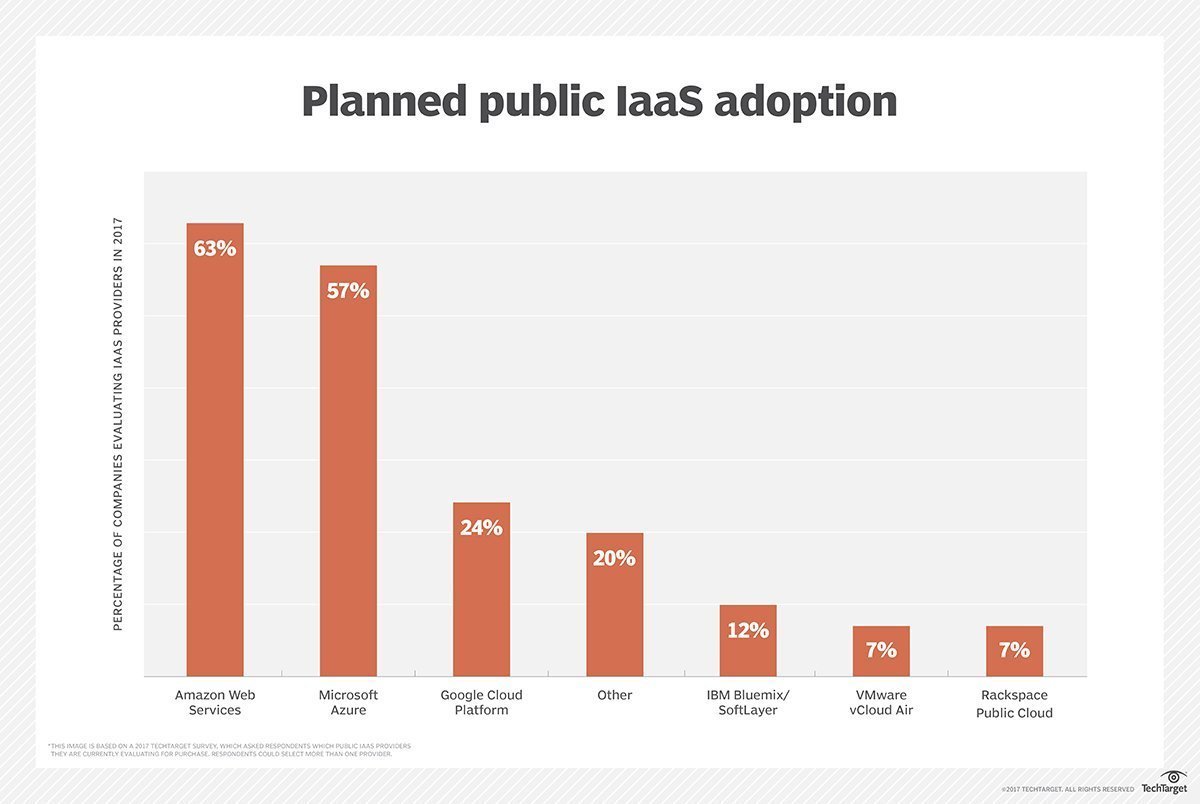
Public cloud providers and adoption
The public cloud market is led by a few key players, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. These providers deliver their services over the internet and use a fundamental pay-per-usage approach. Each provider offers a range of offerings oriented toward different workloads and enterprise needs
Examples of Public Cloud
The most salient examples of cloud computing tend to fall into the public cloud model because they are, by definition, publicly available. Examples include:
- Cloud storage services
- Online software applications
- Cloud hosting, including website hosting
- Cloud based development environments
To some extent they can be defined in contract to private clouds which ring-fence the pool of underlying computing resources, creating a distinct cloud platform to which only a single organisation has access. Public clouds, on the other hand, provide services to multiple clients using the same shared infrastructure. Public clouds are used extensively in offerings for private individuals who are less likely to need the level of infrastructure and security offered by private clouds. However, enterprises can still utilise public clouds to make their operations significantly more efficient, for example, with the storage of non-sensitive content, online document collaboration and webmail.

